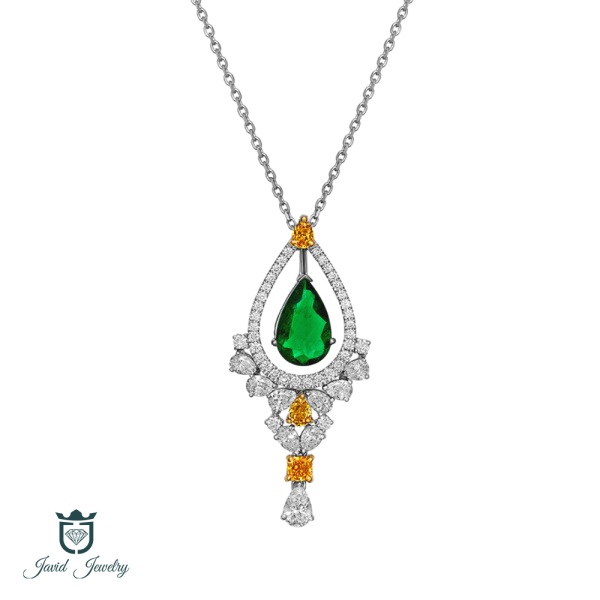
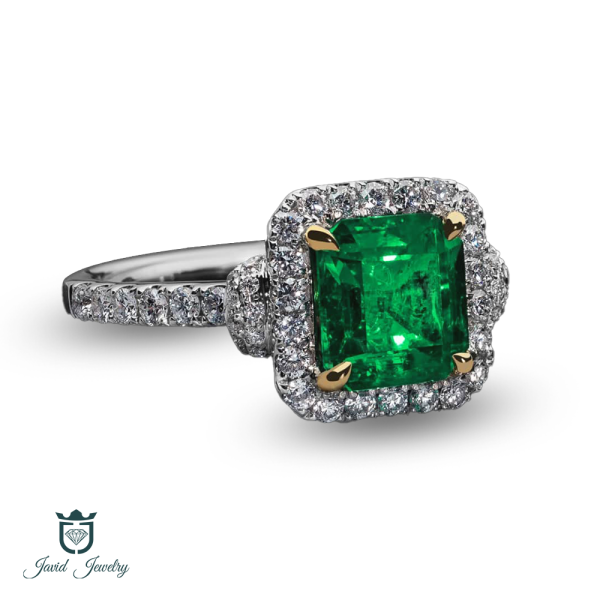
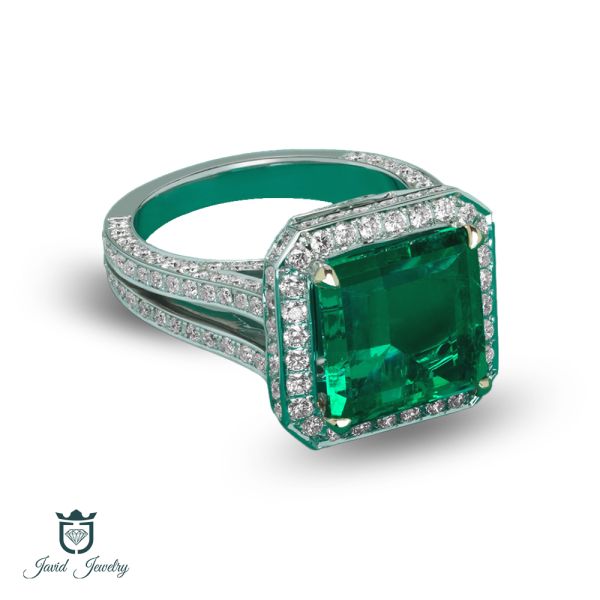
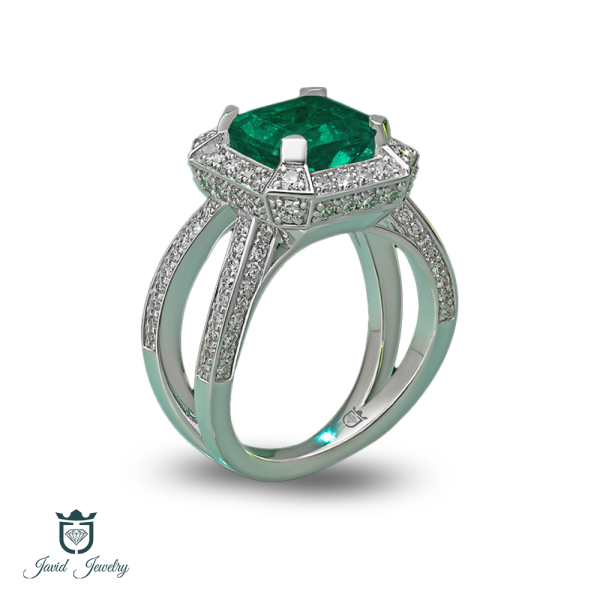
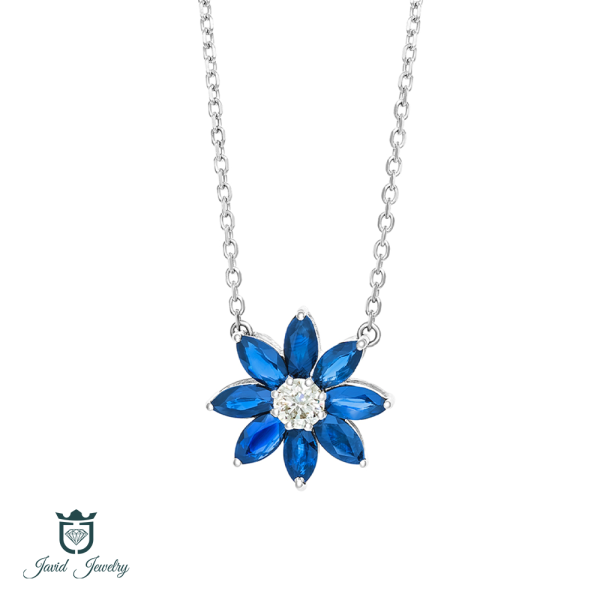
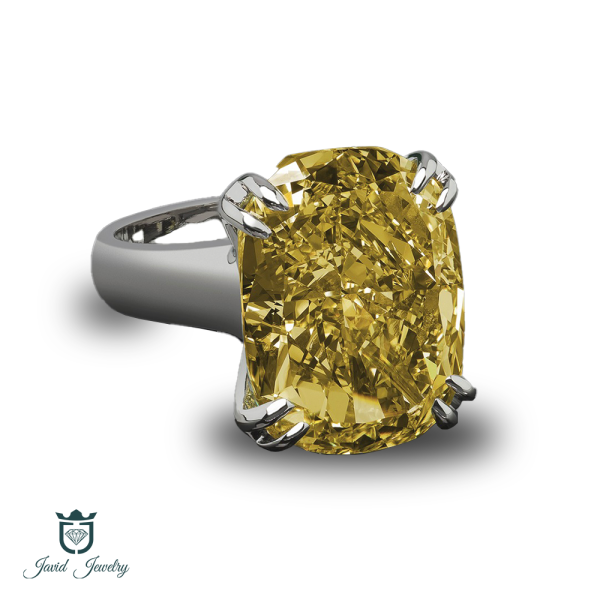
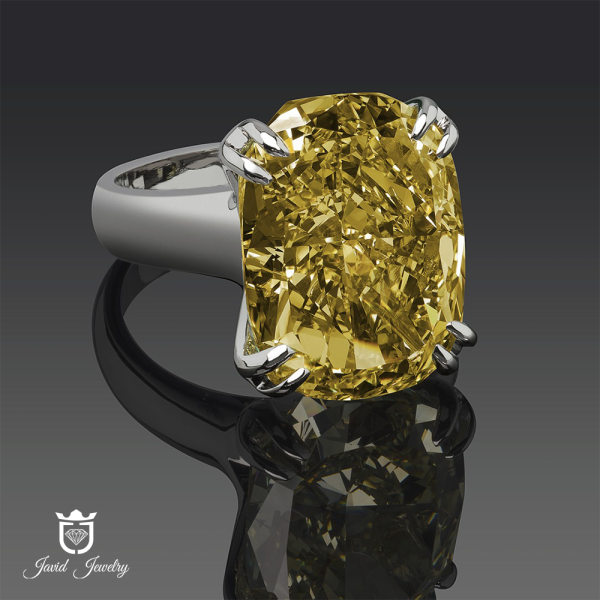
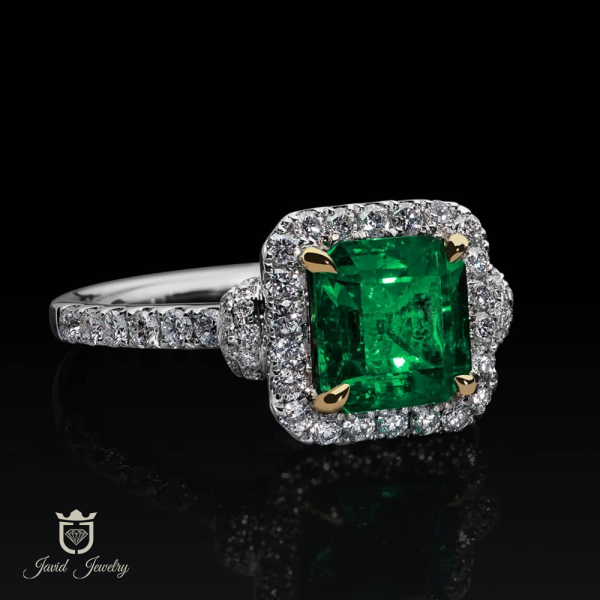
CATALOGUE
Our Products
Special OffersBest Selling
New Arrivals
Create Your Own
Custom Diamond Jewelry
Create Your Own
Custom Diamond Jewelry
Love Inspires
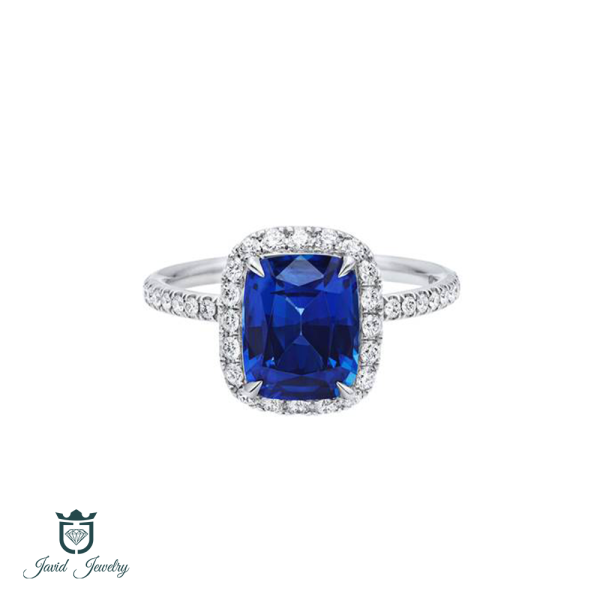
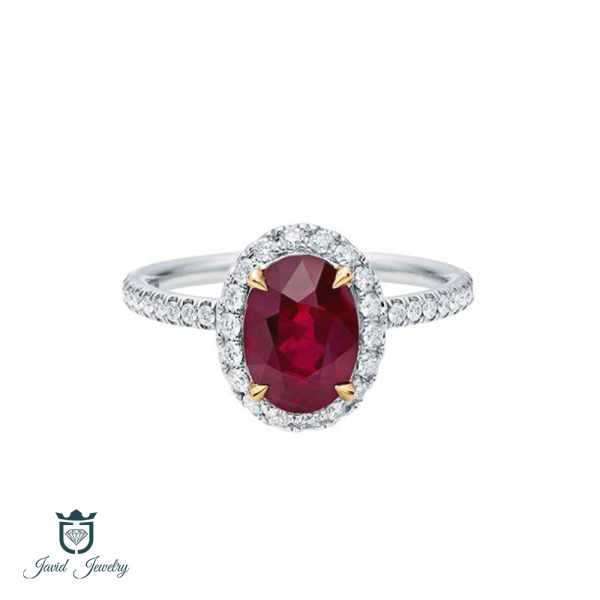
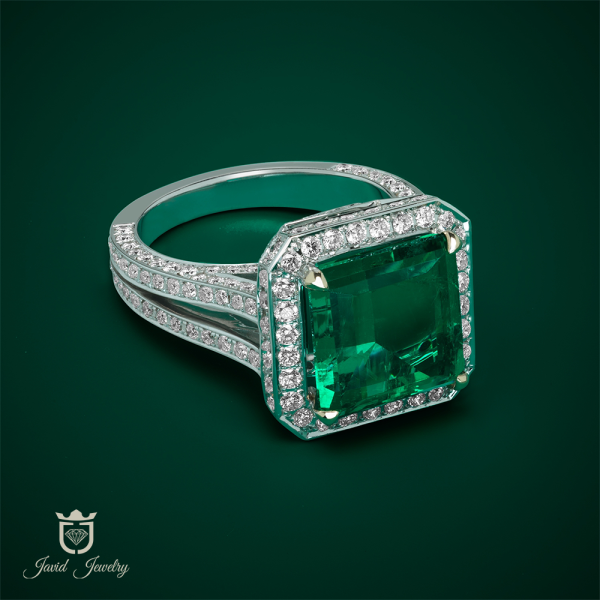
Engagement Rings
Wedding & Engagement
We can help you to find your wanted rings in best price, just click on continue and explore thousand of rings ready for you.
ContinueNeed Gift ?
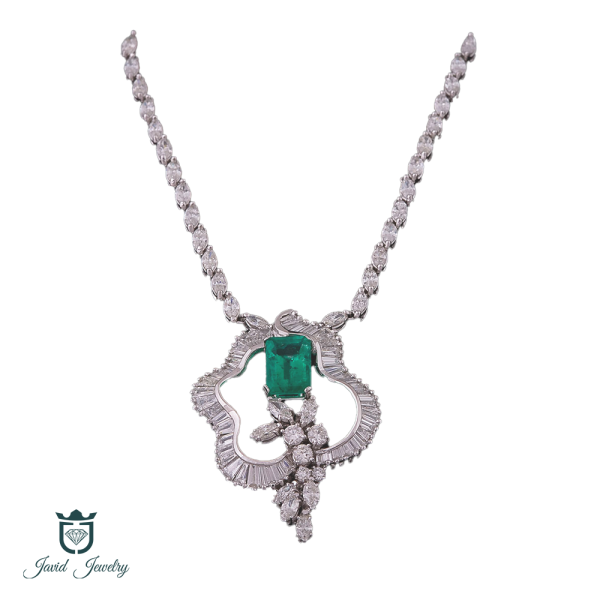
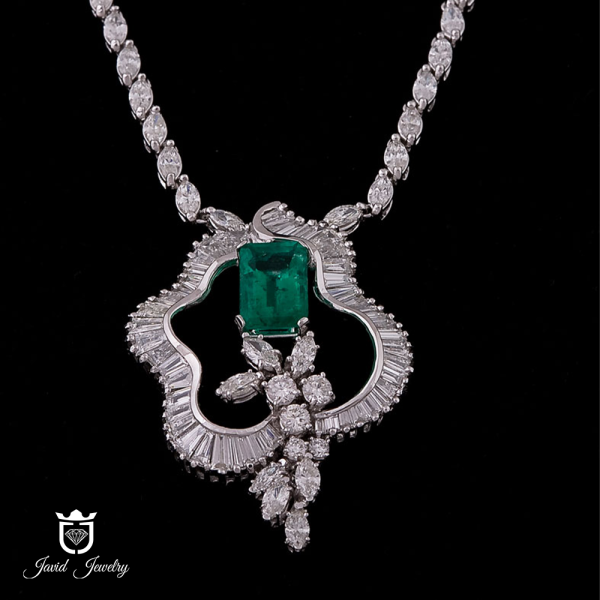
Gift Guide
Gift Guide
We can help you to find your wanted gift in best price, just click on continue and explore thousand of gifts ready for you.
ContinueLove Inspires
Engagement Rings
Wedding & Engagement
We can help you to find your wanted rings in best price, just click on continue and explore thousand of rings ready for you.
ContinueNeed Gift ?
Gift Guide
Gift Guide
We can help you to find your wanted gift in best price, just click on continue and explore thousand of gifts ready for you.
ContinueThe 4Cs:
- Carat Weight:
- Refers to the size or weight of the diamond.
- Measured in carats, where 1 carat equals 0.2 grams.
- Larger diamonds are rarer and usually more valuable.
- Cut:
- Describes how well the diamond is shaped and faceted.
- The cut determines the diamond’s brilliance, sparkle, and overall aesthetic appeal.
- Grading ranges from Excellent to Poor.
- Color:
- Evaluates the absence of color in a diamond.
- Graded on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (noticeable yellow or brown tint).
- The closer a diamond is to being colorless, the higher its value.
- Clarity:
- Measures the presence of internal flaws (inclusions) and external blemishes.
- Graded on a scale ranging from Flawless (no inclusions visible under 10x magnification) to Included (visible inclusions).
- Diamonds with fewer flaws are rarer and more valuable.




History of the 4Cs:
The 4Cs were developed in 1953 by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) to create a universal standard for diamond grading. Before this, diamond quality assessments were inconsistent and often subjective.
- Why the GIA introduced the 4Cs:
- The diamond market needed an objective and transparent way to grade and compare diamonds.
- Jewelers could confidently describe the qualities of a diamond to customers.
- Customers gained a clear understanding of what they were purchasing.
- Impact:
- The 4Cs revolutionized the diamond industry by ensuring consistency and trust.
- Today, the 4Cs are the global standard for diamond grading and remain a critical part of the diamond-buying process.